The aim of this project
is to look at the advantages and disadvantages of renewable energy and what are
they. Our sources include facts and figures from several websites.
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources, which are naturally replenished on a human timescale, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat. Renewable energy often provides energy in four important areas: electricity generation, air and water heating/cooling, transportation, and rural(off-grid) energy services.
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources, which are naturally replenished on a human timescale, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat. Renewable energy often provides energy in four important areas: electricity generation, air and water heating/cooling, transportation, and rural(off-grid) energy services.
Now, we are going to explain the following renewable energies:
SOLAR ENERGY is
radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of
ever-evolving technologies such as solar heating, photovoltaics, solar thermal energy, solar
architecture, molten salt power plants and artificial photosinthesis.
It is an important source of renewable energy and its
technologies are broadly characterized as either passive solar or active solar
depending on how they capture and distribute solar energy or convert it into
solar power.
·
Photovoltaic solar
panels are made up of materials capable of
producing electricity when the Sun's rays hit them.
·
Thermal solar collectors
are used to heat water, which can either
be used directly or indirectly, upon making turbines rotate and thereby
generate electricity.
WIND POWER is the use of air flow through wind turbines to
provide the mechanical power to turn electric generator 4 and traditionally to
do other work, like milling or pumping. Wind power, as an alternative to
burning fossil fuels , is plentiful, renewable , widely distributed, clean ,
produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, consumes no water, and
uses little land. The net effects on the environment are far less
problematic than those of fossil fuels sources.
Wind farms consist of many individual wind turbines,
which are connected to the electric power transmission network.
1.
The blades turn, propelled by the wind and
transfer their movement to the shaft.
2.
The movement of the shaft passes to the
multiplier, where an adequate turning speed for the generator is reached.
3.
Then, the generator transforms this mechanical
energy into electrical energy.
4. The energy produced moves through conductors cables to
a transformer and from there, flows to the distribution network.
HYDRAULIC ENERGY is the water which has a certain wieght. As a fluid it
is able to move and adapt to the volume that contains it. A river is an example
of this behaviour of water.
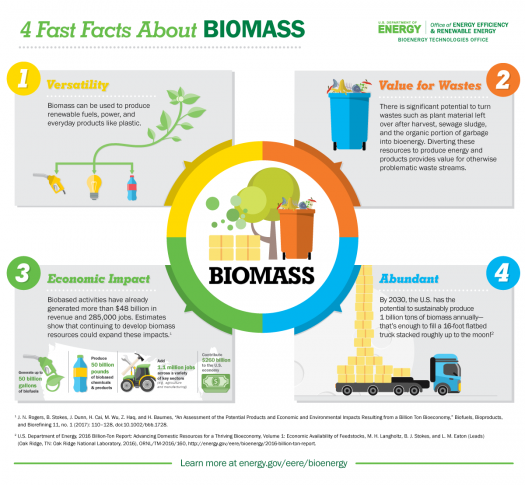
BIOMASS is plant or animal material used for energy
production, heat production, or in various industrial processes as raw material
for a range of products.
FUEL CELLS. A fuel cell is an
electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often
hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair
of redox reactions.Fuel cells are different from most batteries in requiring a
continuous source of fuel and oxygen (usually from air) to sustain the chemical
reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical.
GEOTHERMAL ENERGY. Geothermal energy is
thermal energy generated and stored in the Earth. Thermal energy is the energy
that determines the temperature of matter. The geothermal energy of the Earth's
crust originates from the original formation of the planet and from radioactive
decay of materials.
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
Advantages: it
is a clean energy source, without waste products and is easy to store. Also the
water stored in reservoirs situated at altitude permits the regulation of the
flow of the river.Other advantages of renewable energies is that it can’t run
out and it is very abundant so it can be found in the majority of+ places.It makes the region more autonomous, since it develops
in the same region where it is installed, industry and the economy.
Disadvantages: the construction of hydroelectric plants is expensive
and needs large networks of power cables. Reservoirs also mean the
loss of productive soil and fauna due to the flooding of their habitat. They
also cause a decrease in the flow of the rivers and streams below the dam
and alter the quality of the waters. The following animation shows how
hydraulic energy is stored and exploited.Renewable energy may be a better
option for emission creation than fossil fuels but that doesn’t mean they are
free from pollution.Also it can take a lot of espace to be installed.
USES OF RENEWABLE
ENERGIES IN SPAIN
Electricity from renewable sources in Spain
represented 42.8% of electricity demand coverage during 2014. The country has a
very large wind power capability built up over many years and is one of the
world leaders in wind power generation.
Initially Spain also positioned itself as a European
leader in solar power, by 2007-2010 the country was second only to Germany in
installed capacity, however other countries (Italy in particular) have since
leapfrogged Spanish development. By 2015 solar power in Spain though
significant produced less than a third of that of wind power in 2015.
Spain has set the target of generating 20% of all its
energy needs from renewable energy sources by 2020 and an additional 0.8% may
be available for other EU countries under the cooperation mechanism bringing
the total to 20.8%. By the end of 2014 Spain had reached a level of 16.2% of
all its energy needs from renewable energy sources.
The story of renewable energy development in Spain is
both a mixed and unfinished one. Under previous subsidies the country expanded
its renewable base rapidly and helped establish a domestic industry in both
wind turbine and solar energy. However, support was drastically cut back
following the global financial crisis and new installations stagnated between
2012 and 2015. The debts incurred during the boom period have led to tougher
and retrospective revisions of contracts to providers of renewable energy
reducing returns considerably. In being one of the first-to-market countries,
Spain faces the challenge of powerful competitors from countries such as
Denmark, Germany and China and ironically a cheaper and more mature renewable
energy sector which Spain itself helped to pioneer.
By: Paula Capel, Hugo Expósito, Alba María Molina and
Arturo Beléndez.

Comentarios
Publicar un comentario